Medigap, Medicare Advantage, Plans A through N—choosing the right insurance plan can be overwhelming and confusing. Here's a primer to help take the mystery out of Medicare supplemental insurance.
What is Supplemental Insurance?
Medicare supplemental insurance (also known as Medigap) picks up where Original Medicare (Parts A and B) leaves off. It pays for medical expenses that Medicare does not cover, such as copayments, coinsurance and deductibles.
Medigap plans are sold by private insurance companies to fill "gaps" in Medicare plan coverage. There are 10 standardized plans available in most states, labeled Plan A through Plan N. Each offers a different set of benefits. Note that Massachusetts, Minnesota and Wisconsin standardize their Medigap differently from the rest of the states.
All private insurance carriers who offer a given Medigap plan must offer the same standardized level of coverage. This makes it easier to compare plans. However, insurance carriers compete with each other on customer service, monthly premiums, or other features you may care about.
Here is a side-by-side comparison of plans A through N:
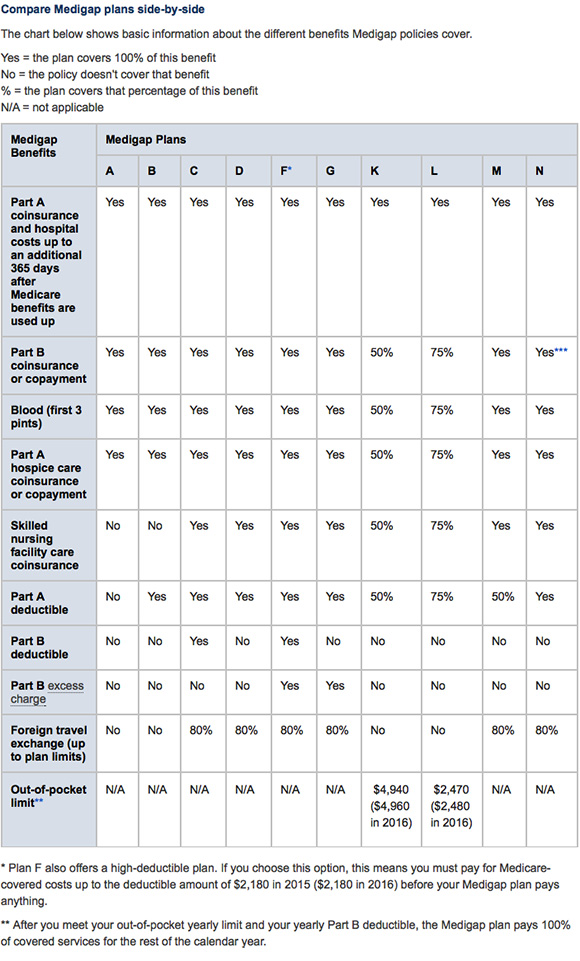
Although these supplemental plans can offer more comprehensive coverage than Medicare Parts A and B alone, they generally don't cover long-term care, vision or dental care, hearing aids, eyeglasses, or private-duty nursing. Drug coverage varies by plan as well. You may need to opt for an additional Medicare Part D Plan for ensure your prescriptions are covered. Keep in mind that you cannot have a Medicare Advantage Plan and Medigap simultaneously.
For more information on insurance to supplement Medicare, visit www.medicare.gov.